If you're reading this, there’s a chance you’re new to telecom and its long list of acronyms. In this article, we’ll demystify some of the most commonly used telecom terms: MNO, MVNA, MVNE and MVNO, and explore how, by working with an end-to-end platform and leveraging modern APIs and automation, mobile brands can bypass complexity, reduce capital expenditure and create beautiful user experiences for their customers.
What is a Mobile Network Operator (MNO)?
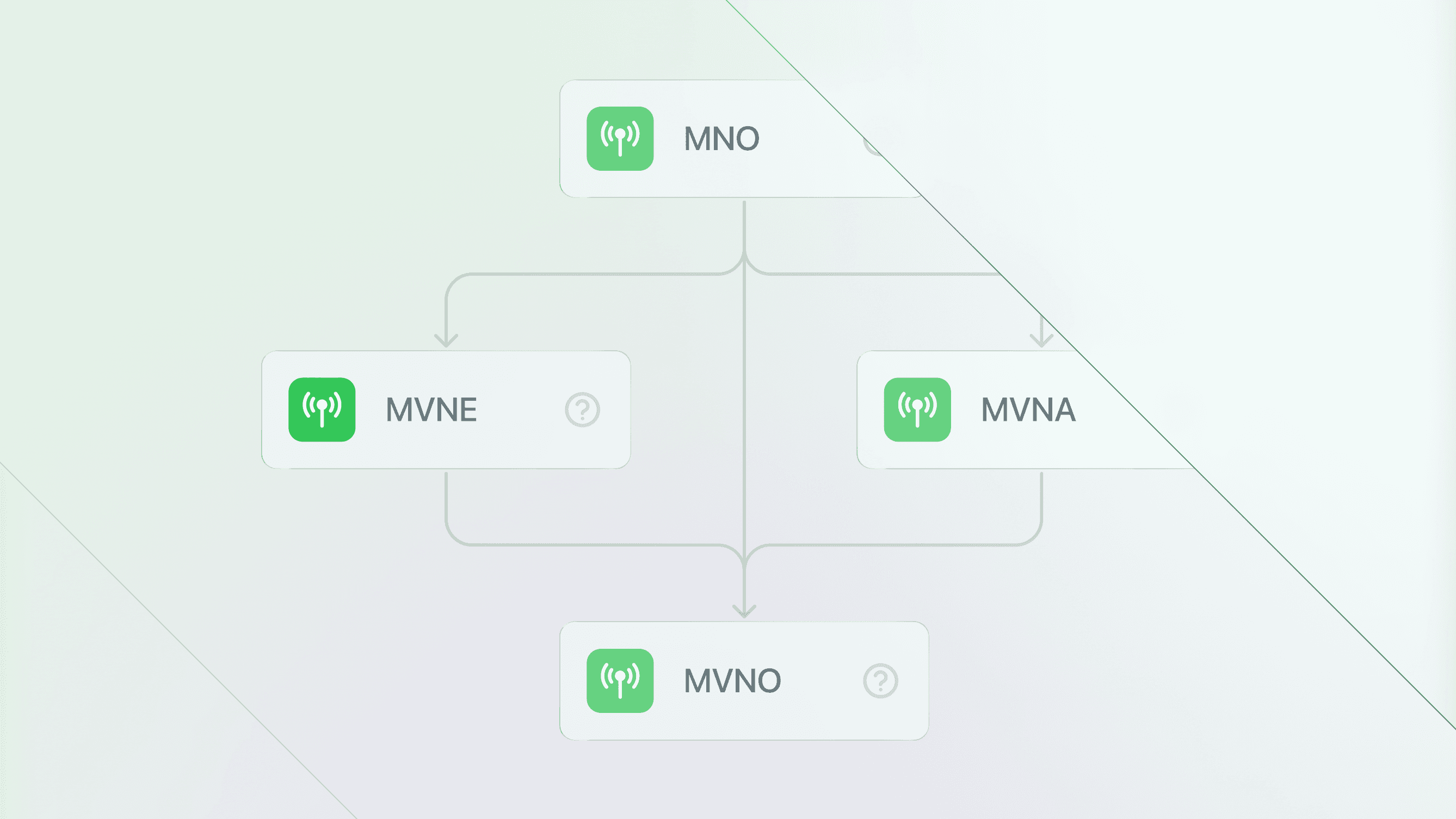
A Mobile Network Operator (MNO) is a company that owns, or at least own licenses for, the network infrastructure that enables wireless connectivity. MNOs are also called carriers, mobile service providers, or simply networks. Examples of MNOs include Verizon, AT&T, and T-Mobile.
As well as selling mobile plans directly to consumers, MNOs sell connectivity at wholesale rates to Mobile Virtual Network Operators (MVNOs), such as Mint Mobile and Consumer Cellular, which then sell on to end users. This relationship benefits all parties.
MNOs can reach new demographics with no acquisition costs.
MNVOs can launch their own phone plans tailored to specific customer segments.
End users are given a greater choice of mobile provider and more flexibility when it comes to picking their phone plan.
MNOs operate a tiered pricing model and MVNOs that work directly with them are required to buy large quantities of wholesale connectivity upfront (and take on the associated risk) in order to secure the best rates. As giants of the telecom industry, MNOs also tend to move slowly. It can take several months to negotiate a partnership with an MNO and the cost of integration is immense. Each MNO has it's own proprietary network integrations, leading to significant additional costs for companies that wish to run their mobile service on more than one network.
Fortunately, there are alternative ways to purchase wholesale connectivity.
What is a Mobile Virtual Network Aggregator (MVNA)?
A Mobile Virtual Network Aggregator (MVNA) buys wholesale mobile and data services from MNOs and sells them to MVNOs. Because MVNAs buy connectivity in bulk, they can sell it for a better price than smaller MVNOs will get by going direct to an MNO.
While buying connectivity from an MVNA may save your company money versus buying direct from an MNO, MVNAs still require upfront volume commitments, and integration with legacy MVNA systems will take time and require dedicated engineering support.
What is a Mobile Virtual Network Enabler (MVNE)?
Mobile Virtual Network Enablers (MVNEs) supply operational and business support systems to MVNOs. Examples of services that MVNEs provide include:
Billing and CRM solutions: Managing billing and customer relationships can be resource-intensive without proper software. MVNEs provide telecom billing software and telecom CRM tools designed to streamline the customer experience.
Provisioning and SIM management: The logistics of provisioning SIM cards and eSIMs can be complicated. MVNEs handle this process for MVNOs, ensuring a seamless activation experience for customers.
Regulatory compliance: The telecom industry is highly regulated. MVNEs ensure that all legal requirements and customer protections are adhered to, reducing the risk of non-compliance.
Within the telecom industry, the operational systems that MVNEs supply are known collectively as OSS and BSS.
Many MVNE providers claim to deliver end-to-end services, but in most cases their offerings are not fully comprehensive. As a result, you may need to collaborate with multiple providers to manage the various aspects of your operations. This can lead to a lack of cohesion and a cycle of dependencies, where solving one issue creates another. For example, adjusting your billing system with one provider might cause compatibility problems with your CRM system from another, making it challenging to maintain agility and foster innovation, particularly as you scale.
Gigs was designed to tackle this problem. Our platform provides everything you need to launch a mobile service on a global scale via a single integration. From multi-carrier wholesale connectivity to billing, subscription management, compliance and more.
What is a Mobile Virtual Network Operator (MVNO)?
A Mobile Virtual Network Operator (MVNO) is a company that sells talk, text, and data to everyday consumers. But, unlike MNOs, MVNOs do not own the wireless network infrastructure, and instead purchase wholesale connectivity directly from MNOs or from other third parties.
By outsourcing the technical, operational and regulatory complexities of running a wireless service, these "white label MVNOs" can concentrate on creating a compelling brand, developing innovative offerings, and delivering exceptional experiences to their customers.
The MVNO business model has enabled multiple brands, including Mint Mobile, Cricket Wireless and Consumer Cellular to amass millions of customers.
Recent advances in telecom APIs have prompted new players to enter the telecom game—from major neobanks like Nubank to startups like Light. With the right partner, these brands can cut out all of the technical and regulatory complexity of launching and running a mobile service, and focus on creating connectivity solutions that are tailor made for their target audience.
For example, a family-focused fintech could offer phone plans tailored to the under-18s market, a travel brand could offer free travel eSIMs to their premium members, and an HR tech platform could offer workplace phone plans to their corporate clients.
This opens up exciting possibilities for the future of telecom, ushering in an age where connectivity is seamlessly embedded in the digital services we use daily, delivered by a brand that we trust.
The benefits of an end-to-end mobile operating system
Historically, before launching a mobile service, companies had to negotiate with MNOs or MVNAs to acquire wholesale connectivity, then work with a host of MVNEs to manage billing, subscriptions, customer service, regulations, taxes, and more.
As the world’s only end-to-end telecom operating system, Gigs was designed to abstract that complexity, offering everything your company needs to launch and scale a wireless service across multiple markets, carriers and use cases.
 End-to-end connectivity platformWith unparalleled automation, world-class UX, and superior conversion rates, Gigs not only minimizes launch costs but drastically reduces operating expenses. With our multi-network API, it’s possible to launch a premium wireless service on a global scale in a matter of weeks.
End-to-end connectivity platformWith unparalleled automation, world-class UX, and superior conversion rates, Gigs not only minimizes launch costs but drastically reduces operating expenses. With our multi-network API, it’s possible to launch a premium wireless service on a global scale in a matter of weeks.
To learn more about how we can help your business launch and scale a mobile service, speak to our team.